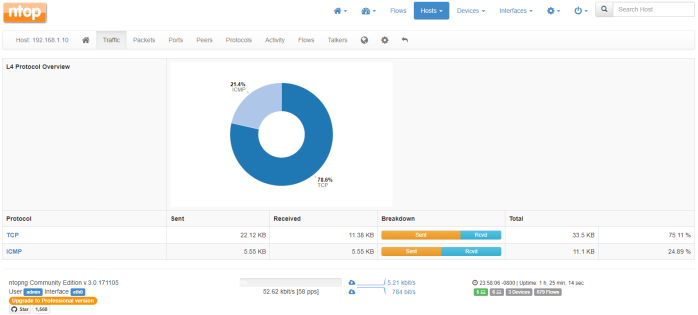
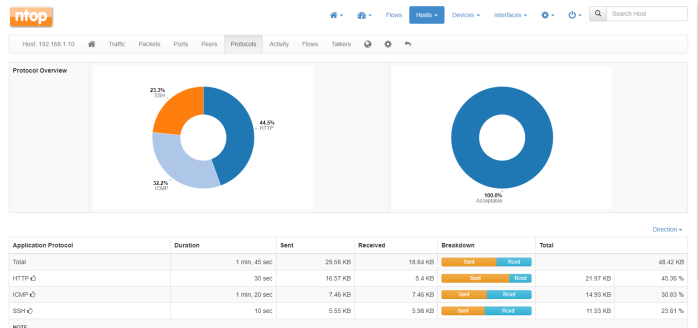
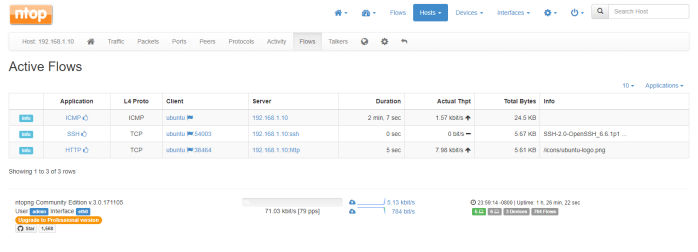
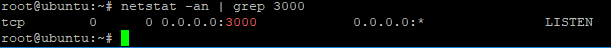Hi guys,
On the previous article i was writing about SDN Concept using Mininet emulator, now we will explore about OpenDaylight Platform, wait…what is that?? OpenDaylight Platform previously named OpenDaylight Controller, so basicly OpenDaylight is open source SDN controller hosted by linux foundation.
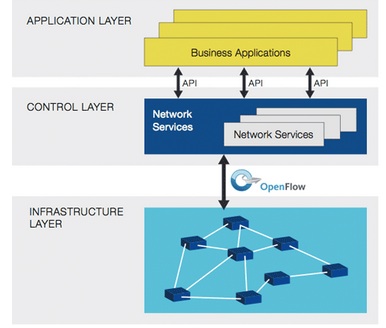
The OpenDaylight Controller exposes open northbound APIs, which are used by applications. These applications use the Controller to collect information about the network, run algorithms to conduct analytics, and then use the OpenDaylight Controller to create new rules throughout the network. (Source : sdxcentrall.com)
for the southbound communication OpenDaylight includes support for the OpenFlow protocol, but can also support other open SDN standards (Remember 3 Layer architecture Of SDN concept)
okay, the main point of this article i will try to install OpenDaylight Platform as SDN controller to my mininet emulator which I have installed before (you can read how to installed mininet on the previous article)
as usuall i will installed OpenDaylight on my ubuntu 14.04 AMD64 with minimum specification, because this is for testing purposes
a. Specification Requirement:
CPU : 2 Core
RAM : 4 GB
DISK : 40 GB
b. Software Requirement :
Latest Java (Ver 7 – 8) because OpenDaylight Platform writing used JAVA Programming language)
apache-maven-3.3.3
OpenDaylight Package
c. Installation Step :
1. Update Repository and Install JAVA 8:
#sudo add-apt-repository ppa:webupd8team/java -y
#sudo apt-get update
#sudo apt-get install oracle-java8-installer
2. Download Maven package and Configure to the system
Downoad pakage maven used command
create folder “apache-maven” on directory /usr/local
#mkdir -p /usr/local/apache-maven/
move package maven to folder directory apache-maven
#mv apache-maven-3.3.3-bin.tar.gz /usr/local/apache-maven/
extract package maven with command :
#tar -xzvf /usr/local/apache-maven/apache-maven-3.3.3-bin.tar.gz -C /usr/local/apache-maven/
Configure maven
# sudo update-alternatives –install /usr/bin/mvn mvn /usr/local/apache-maven/apache-maven-3.3.3/bin/mvn 1
# sudo update-alternatives –config mvn
3. Configures ~/.Bashrc to update path of your JAVA home Directory and Maven Directory
# sudo apt-get install vim
# vim ~/.bashrc
Add this on the end of line
export M2_HOME=/usr/local/apache-maven/apache-maven-3.3.3
export MAVEN_OPTS=”-Xms256m -Xmx512m”
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-8-oracle
used config ~/.bashrc to your system
#source ~/.bashrc
4. and check your Java Home Directory with command
#echo $JAVA_HOME
5. Next we will download OpenDaylight Package from their website, i choose new update ODL “Carbon SR1” on “July 14, 2017”
before we start OpenDaylight Controlelr, if you already have openvswitch on your system, stop the service with comamnd
#service openvswitch-controller stop
#service openvswitch-switch stop
6. Next step we will start OpenDaylight Controller, first unzip OpenDaylight package we have downloaded
#unzip distribution-karaf-0.6.1-Carbon.zip
7. Run OpenDaylight with command
#cd /distribution-karaf-0.6.1-Carbon/bin
#./karaf
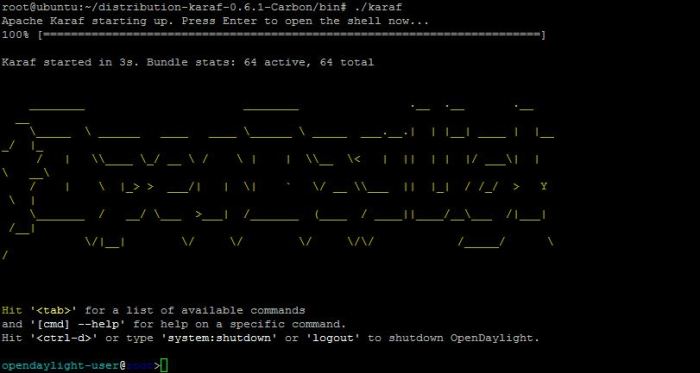
on this step, we have success running OpenDaylight SDN controller on our linux system, next from the OpenDaylight comamnd line we will install odl-l2switch and OpenDaylight User Experience (DLUX) application. DLUX is an openflow network management application for Opendaylight controller. this installation feature to add web interface on OpenDaylight Platform, can login to web interface and control Southbound connections to OVS (Open Virtual Switch) with OVSDB to learn MAC address from host connected to the switch
8. Install feature needed by opendaylight
opendaylight-user@root>feature:install odl-l2switch-switch-ui
opendaylight-user@root>odl-dlux-core
opendaylight-user@root>odl-dluxapps-nodes
opendaylight-user@root>odl-dluxapps-topology
opendaylight-user@root>odl-dluxapps-yangui
opendaylight-user@root>odl-dluxapps-yangvisualizer
opendaylight-user@root>odl-dluxapps-yangman

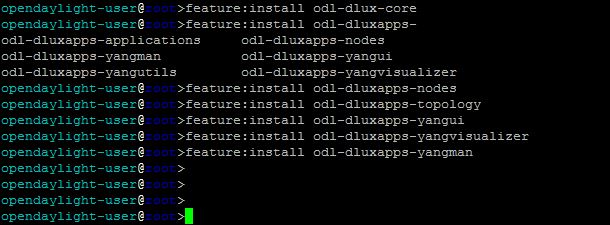
9. after add all feature needed by OpenDaylight (ODL) , you can check port listening of your ODL system with command :
#netstat -an | grep tcp
make sure you can see port TCP:8181 as port service to access web interface OpenDaylight, TCP:6633 and TCP:6653 (Port Service Communication for OpenFlow)
d. Access OpenDaylight Platform
To Access OpenDaylight Platform as SDN Controller type on your URL browser
<IP address OpenDaylight>:8181/index.html
ex : 192.168.98.211:8181/index.html (dont forget type till the path index.html)
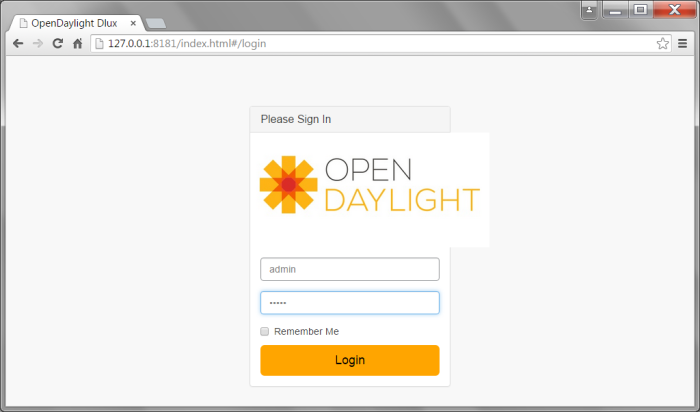
login to the OpenDaylight controll used default cridential
user : admin
pass : admin
and you will be shown main page of OpenDaylight controller like on the picture below
e. Integrate OpenDaylight to Mininet as SDN Controller
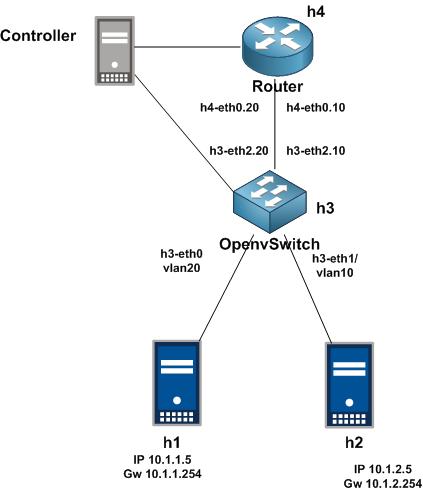
at this stage we have success to run OpenDaylight Platform and access OpenDayligt website interface (DLUX), next step we will integrate our Mininet SDN emulator to OpenDaylight Platform as SDN Controller through Simple topology
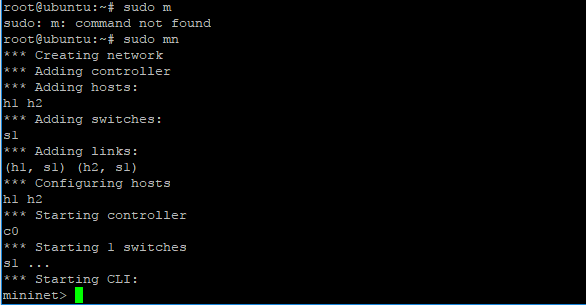
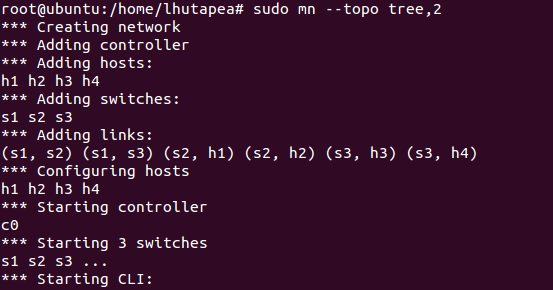
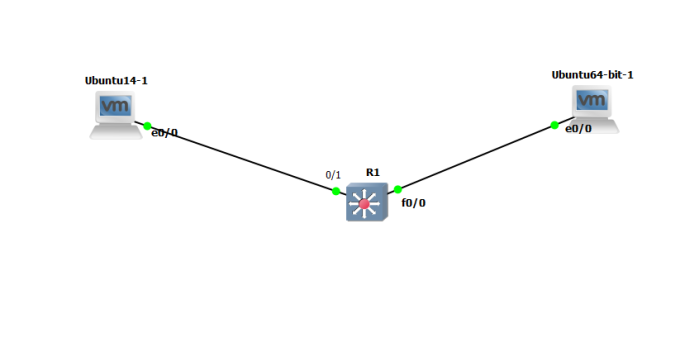
Login to your mininet Virtual Machine, and create simple topology used mininet emulator with OpenDaylight Platform as Remote Controller SDN with command
root@mininet#sudo mn –topo tree,2 –controller remote,ip=192.168.98.211
Note : 192.168.98.211 is IP address OpenDaylight Platform
from command above, mininet will create 3 OpenVSwitch, 4 host and 1 Remote Controller. after execute that command, we can back to web interface opendaylight to see topology information from mininet. click 3 Bar near logout button on top right corner and choose topology like example picture below
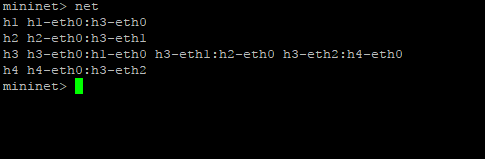
and we can see topology on mininet configuration from command execution before
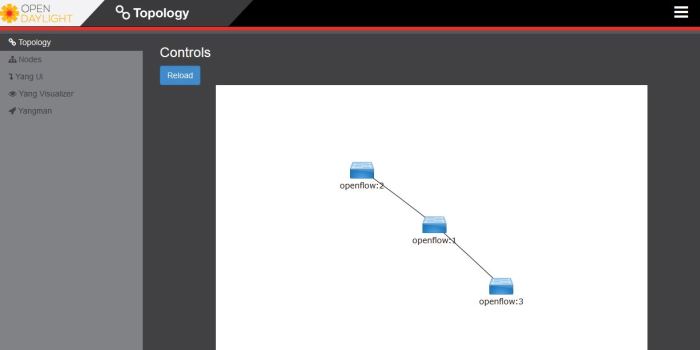
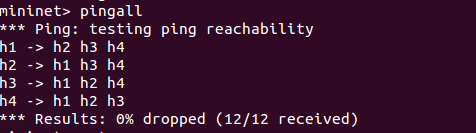
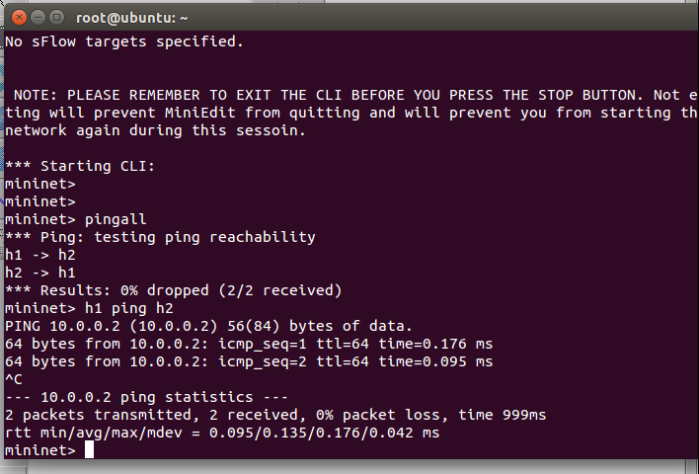
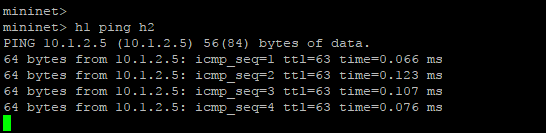
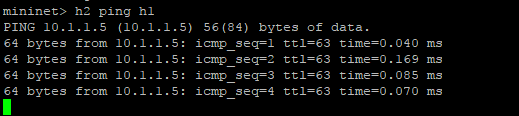
from execution command before, we know mininet will created 3 OVS and 4 host on network emulator, but on topology OpenDaylight controller, we just see 3 OVS and can not find 4 host connected to OVS, this happen because OVS need obtaining the MAC address to identifying host conencted to they interface. So from mininet command line interface do Ping to all host on mininet topology with command
mininet>pingall
back to topology OpenDaylight and click reload button to refresh topology information , now we can see on OpenDaylight Topology there 4 hosts connected to OpenVSwitch like on the picture below
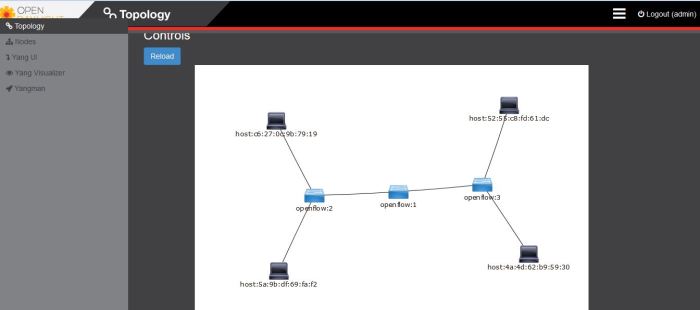
That’s all i can share to you on this article, hope this informative for you and thank you